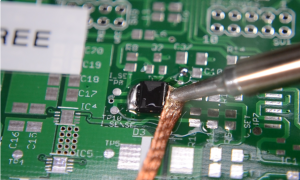
Soldering is one of the essential processes that fix the components into a printed circuit board. It affects PCB quality and capabilities. In the PCB manufacturing factory, staff operate the soldering machine and check after the soldering by AOI machine or X-ray inspection machine to avoid soldering problems occur on finished PCBA boards.
For electronics makers or newbies, hand soldering has always been considered a trait skill to have. However, even with the specialist or automatic machine soldering, problems may have appeared. This article is a guide for PCB soldering
- Solder Bridges:
Solder bridges are unwanted excess solder connections between adjacent solder joints, which can lead to circuit shorts. To avoid solder bridges, it’s crucial to choose the right soldering tools (such as soldering stations and tips) suitable for the task, with tip sizes matching the size of the solder joints. During soldering, control the amount of solder applied to prevent unwanted connections between adjacent solder points. After soldering, carefully inspect using a magnifying glass or microscope to ensure no solder bridges are present.
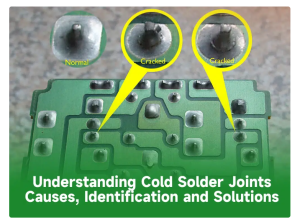
- Cold Solder Joints:
Cold solder joints occur when the solder fails to fully melt and form a secure connection with the solder joint. This is often caused by impure solder, insufficient soldering temperature, or too short soldering time. To prevent cold solder joints, use high-quality solder and ensure the soldering temperature is sufficient. Additionally, maintain a sufficient soldering time to allow the solder to fully melt and form a stable connection with the solder joint.
- Excessive Solder:
Using too much solder not only wastes material but can also result in oversized solder joints, affecting the layout and aesthetics of the circuit board. Excessive solder can also mask potential issues such as dry joints or cold solder joints. Therefore, it’s essential to control the amount of solder applied during soldering, ensuring that the solder joint is both sufficient and not excessive. - Insufficient Solder:
Insufficient solder can lead to weak joints that are prone to falling off or disconnecting. To avoid this, ensure that adequate solder is applied during soldering to create a solid and secure joint. Also, pay attention to the soldering time, avoiding too short durations that prevent the solder from fully melting.
- Heat Damage:
Excessive soldering temperature or prolonged soldering can cause thermal damage to the circuit board or components. To prevent this, use soldering tools with temperature control and select appropriate soldering temperatures based on the type of components and circuit board. Avoid lingering in the same spot for too long during soldering to minimize the risk of thermal damage.
- Improper Soldering Sequence:
An improper soldering sequence can lead to issues such as solder bridges or component displacement. To ensure soldering quality, follow a certain soldering sequence, typically starting with low-profile, heat-resistant components and moving on to taller, less heat-resistant ones. This helps reduce interference and damage during the soldering process. - Dirty Work Area:
Dust, oil, and other contaminants in the workspace can adhere to the solder joints, affecting soldering quality. Therefore, keep the workspace clean and tidy, regularly cleaning the soldering station and tools. Before soldering, ensure that the circuit board and components are clean to prevent contaminants from affecting soldering quality. - Improper Component Placement:
Improper placement of components can make soldering difficult or result in poor soldering quality. When placing components, ensure they are correctly aligned and positioned, avoiding issues such as tilting or misalignment. For small components, use tools like tweezers for assisted placement to ensure stability and accuracy. - Improper Handling of Circuit Boards:
Improper handling of circuit boards during soldering can lead to fractured solder joints or component detachment. Avoid excessive bending or twisting of the circuit board to prevent such damage. After soldering, store the circuit board properly to protect it from physical damage or chemical corrosion.
10 Lack of Inspection:
Failing to conduct necessary inspections can lead to overlooked potential issues, compromising the final quality of the circuit board. Therefore, after soldering, perform a thorough inspection of the circuit board, including the appearance and connections of the solder joints. Use a magnifying glass or microscope for detailed
observations to ensure that each solder joint meets the requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the main cause of cold solder joints?Cold solder joints are primarily caused by insufficient heat transfer during the soldering process. This can be due to an inadequate soldering iron, improper heat application, or contamination on the surfaces being soldered.
- How can I prevent tombstoning when soldering surface-mount components?To prevent tombstoning, ensure proper solder paste or solder deposition on the component pads, adjust the reflow profile or soldering iron temperature, consider using a solder paste with a higher metal content, and ensure that the component pads are properly sized for the component dimensions.
- What is the best way to remove solder bridges?The recommended method for removing solder bridges is to use a desoldering braid or wick. These materials absorb and remove excess solder, allowing you to eliminate unintended connections between adjacent pads or traces.
- Can overheating components during soldering cause permanent damage?Yes, excessive heat can cause permanent damage to sensitive electronic components. Overheating can lead to physical damage, degradation of performance, or premature failure of the component. Always use appropriate soldering temperatures and apply heat judiciously to prevent overheating.
- Why is it important to remove flux residue after soldering?Leaving excessive flux residue on the PCB can lead to corrosion, short circuits, or insulation breakdown over time, compromising the reliability and performance of the circuit. Proper cleaning with an appropriate flux remover or isopropyl alcohol is essential to ensure long-term durability and functionality.
Hand soldering is a crucial skill in the field of electronics, and mastering it requires practice, patience, and attention to detail. By understanding and avoiding these common PCB hand soldering problems, you can achieve reliable and high-quality solder joints, ensuring the proper functionality and longevity of your electronic projects. Remember to follow best practices, use the right tools and techniques, and prioritize safety throughout the soldering process.